Income tax slab rates plays an important role in the Indian economy and is an important source of revenue for the government. These funds are needed to finance various public services, infrastructure projects and social welfare programmes. Therefore, it is important for every taxpayer in India to have a thorough understanding of taxation, its accountability and wider impact on the private and public finances.

This article takes a closer look at the various income tax categories for the fiscal year(s) 2024, providing a comprehensive analysis of how they have evolved over the last few years By examining these trends, readers can gain insight into the government’s budget and its impact on taxpayers. Furthermore, the article places the Indian income tax system in the broader context of the global economy, offering a comparative perspective on how Indian tax policies overlap or differ from those of other countries.
Understanding the number and proportion of income tax groups is essential for effective budgeting. The article will describe the current slabs, highlight any changes or new introductions, and explain their implications for different income groups. By analysing trends, readers can understand changing government priorities and strategies to address economic challenges and opportunities.
Furthermore, the discussion extends to the overall state of the Indian economy considering factors such as GDP growth, inflation, inflation etc. Putting the Indian income tax system in the global context, the objective of the article is to ensure the country’s economic health and position on the global stage.
This article is a valuable resource for taxpayers, financial analysts, and anyone else interested.
Table of Contents
What are Income Tax Slab Rates?
Income tax slab rates refer to various levels of income and their corresponding tax rates that individuals and corporations have to pay to the government Indian income tax system using a progressive tax system, i.e., when income is taxable goes up, the tax rate goes up. Here is a detailed explanation of income tax in India:
Understanding Income Tax Slabs
Tax units classify taxpayers on the basis of their annual income, and assign specific taxes to each slab. These tablets are designed to ensure that low-income earners pay a higher percentage of their income in taxes than low-income earners.
Slab rates for individual taxpayers
For individual taxpayers, the income tax slabs can vary based on age and residential status. Here are the common categories:
- Individuals below 60 years of age
- Senior citizens (aged 60 years and above but below 80 years)
- Super senior citizens (aged 80 years and above)
Income Tax Slabs for FY 2023-24 (AY 2024-25)
For Individuals Below 60 Years of Age and HUF:
- Up to ₹2,50,000: No tax
- ₹2,50,001 to ₹5,00,000: 5% of income exceeding ₹2,50,000
- ₹5,00,001 to ₹10,00,000: ₹12,500 + 20% of income exceeding ₹5,00,000
- Above ₹10,00,000: ₹1,12,500 + 30% of income exceeding ₹10,00,000
For Senior Citizens (60 to 80 Years):
- Up to ₹3,00,000: No tax
- ₹3,00,001 to ₹5,00,000: 5% of income exceeding ₹3,00,000
- ₹5,00,001 to ₹10,00,000: ₹10,000 + 20% of income exceeding ₹5,00,000
- Above ₹10,00,000: ₹1,10,000 + 30% of income exceeding ₹10,00,000
For Super Senior Citizens (Above 80 Years):
- Up to ₹5,00,000: No tax
- ₹5,00,001 to ₹10,00,000: 20% of income exceeding ₹5,00,000
- Above ₹10,00,000: ₹1,00,000 + 30% of income exceeding ₹10,00,000
Additional Components of Income Tax
In addition to the slab rates, taxpayers must also consider:
- Surcharge: An additional charge on income tax if the income exceeds certain thresholds (e.g., 10% surcharge for income between ₹50 lakh to ₹1 crore, 15% for income above ₹1 crore).
- Cess: A health and education cess of 4% on the total income tax and surcharge (if applicable).
Income Tax Slab Rates for FY 2024
For the financial year 2024, the Government of India has made some changes to the income tax slab rates. Here are the updated rates for different categories of taxpayers:

For Individuals Below 60 Years of Age
- Income up to ₹2.5 lakh: No tax
- Income from ₹2.5 lakh to ₹5 lakh: 5%
- Income from ₹5 lakh to ₹10 lakh: 20%
- Income above ₹10 lakh: 30%
For Senior Citizens (60 to 80 Years)
- Income up to ₹3 lakh: No tax
- Income from ₹3 lakh to ₹5 lakh: 5%
- Income from ₹5 lakh to ₹10 lakh: 20%
- Income above ₹10 lakh: 30%
For Super Senior Citizens (Above 80 Years)
- Income up to ₹5 lakh: No tax
- Income from ₹5 lakh to ₹10 lakh: 20%
- Income above ₹10 lakh: 30%
Key Changes in 2024
- Increase in Basic Exemption Limit: For senior and super senior citizens, the basic exemption limit has been increased to ₹3 lakh and ₹5 lakh respectively.
- Standard Deduction: A standard deduction of ₹50,000 continues to be available for salaried individuals and pensioners.
Trends in income tax over the last few years
The Government of India has revised the income tax rate from time to time to reflect the economic conditions and fiscal policy objectives. Here is an overview of income tax trends over the past few years.
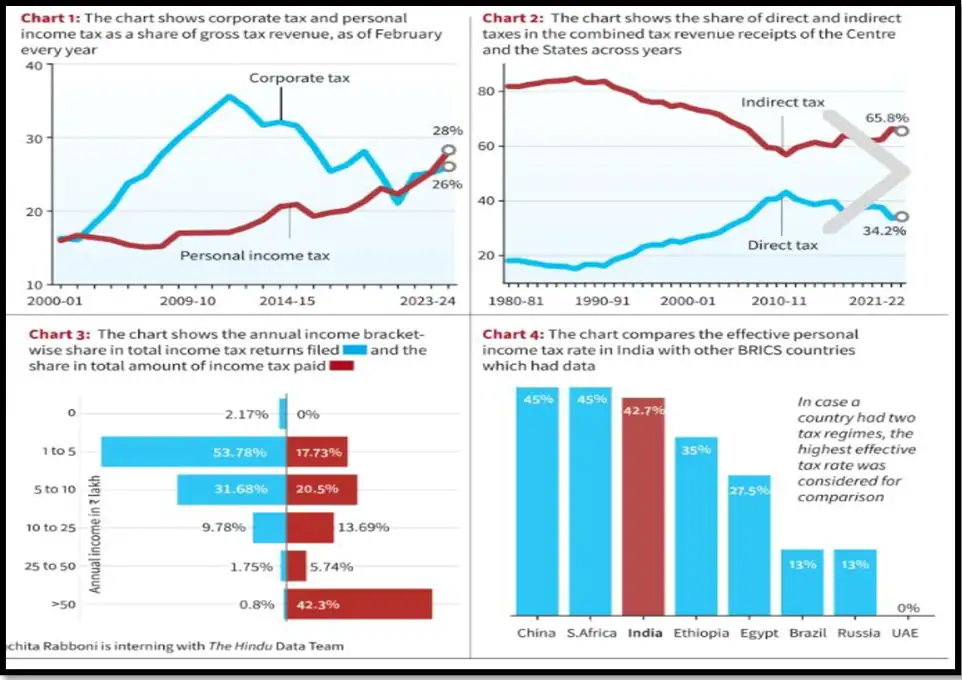
FY 2021-23
- Introduction of new tax regime: A new tax regime with lower rates but without exemptions and deductions will be introduced in FY 2020-21, giving taxpayers a choice between old and new regimes.
- Standard deduction introduced: Standard deduction of ₹40,000 was introduced in FY 2018-19 and later increased to ₹50,000.
FY 2016-2020
- Tax cut for lower income earners: The tax rate for those earning between ₹2.5 lakh and ₹5 lakh has been reduced from 10% to 5% in FY 2017-18.
- Increased for higher income earners: ₹50 lakh Increased surcharges were introduced for individuals earning more than ₹1 crore.
Facts and Figures
- Taxpayer Base Expansion: The number of income tax returns filed has increased significantly, from 3.31 crore in FY 2013-14 to over 6.85 crore in FY 2021-22.
- Revenue Growth: Income tax revenue has grown from ₹2.87 lakh crore in FY 2013-14 to ₹6.49 lakh crore in FY 2020-21.
Position of the Indian Economy in the Global Stand
India is one of the fastest-growing major economies in the world. Here’s a snapshot of its current global standing:
- GDP: India is the world’s fifth-largest economy by nominal GDP and the third-largest by purchasing power parity (PPP).
- Growth Rate: Despite global economic challenges, India has maintained a robust GDP growth rate, with projections of 6-7% growth in FY 2024.
- FDI Inflows: India continues to attract significant foreign direct investment, ranking among the top 10 FDI destinations globally.
- Digital Economy: With rapid digitalization, India is emerging as a leader in digital payments and fintech innovation.
Conclusion
Understanding income tax slab rates is crucial for effective budget planning and compliance. The change in tax rates for 2024 reflects the government’s ongoing efforts to simplify and improve the equity of the tax system. As India continues to grow and consolidate its position in the global economy, there is still a need to inform all citizens about tax policies and their implications.
Hey guys, if you are interested in saving your taxes and taking loans to fulfill your dream you can apply for loans with Shani Finserve Private Limited Apply for Loan Page. For any loan related assistance feel free to contact us.
FREE tools for you:
4 thoughts on “Latest Income Tax Slab Rates in India 2024”